A Complete Guide for Employers and Healthcare Providers
Fentanyl is a potent synthetic opioid that is increasingly involved in drug-related harm and fatalities across the UK and globally. As its misuse continues to rise, employers, occupational health teams, and clinicians must understand how fentanyl appears on drug tests and the best strategies for detection in workplace and clinical settings.
In this article, we explore how fentanyl is detected, what it shows up as on drug tests, how long it stays in the system, and why it’s essential to include fentanyl screening in comprehensive drug testing programs.
What Is Fentanyl?
Fentanyl is a powerful opioid analgesic, up to 100 times stronger than morphine. It is available legally via prescription for severe pain, such as cancer-related pain, but its illicit use—especially in counterfeit pills and mixed with other substances—poses significant danger.
The rise in fentanyl-related deaths is alarming. In recent years, fentanyl has played a growing role in overdose fatalities across the UK. According to the Office for National Statistics, deaths involving fentanyl rose significantly in 2022. Due to its potency, even trace amounts can lead to overdose—particularly when people are unaware that fentanyl has been mixed into other drugs.
Street names include:
- Fenty
- China White
- Dance Fever
- Apache
- Goodfellas
- Jackpot
Will Fentanyl Show Up on a Drug Test?
Yes—fentanyl will show up on a drug test, but it is not always part of standard drug panels. It must be specifically included.
Fentanyl is detected as FYL or FEN on drug test strips, targeting the parent compound or its primary metabolite, norfentanyl.
It can be part of multi-panel drug tests such as:
- 12-panel drug test
- 14-panel drug test
- 16-panel drug test
If you're wondering how long does fentanyl stay in your system or how many days fentanyl stays in your system, the answer varies depending on several factors—covered below.
Which Drug Tests Detect Fentanyl?
Fentanyl Urine Test
- Detection Window: 1–3 days after use
- Use Case: Routine workplace screening, return-to-duty testing, post-incident investigations
- Cut-Off Levels: 1–10 ng/mL (depends on lab and testing kit)
- Advantages: Non-invasive, cost-effective, widely adopted
This is the most common test for fentanyl detection and is widely used across workplace testing programs. Many search how long does fentanyl stay in urine, and the answer can vary slightly depending on the individual and usage patterns.
Fentanyl Saliva Test
- Detection Window: Up to 48 hours
- Use Case: Post-incident testing, random testing, on-the-spot assessments
- Advantages: Quick results, easy to administer
Both test types can detect fentanyl tablets, illicit formulations, and metabolites like norfentanyl.
How Long Does Fentanyl Stay in the System?
Test Type |
Detection Window |
| Urine | 1-3 Days |
| Saliva | 1-2 Days |
Factors that influence how long it takes for fentanyl to leave the system include:
- Frequency and duration of use
- Dosage
- Route of administration (e.g., patch, oral, injection)
- Liver and kidney function
- Individual metabolism
How long does it take for fentanyl to get out of your system?
Generally, within 3 days for occasional use, but chronic use can prolong detection.
Can a False Positive Happen?
Yes, although false positives for fentanyl are rare, they can occur, especially with rapid tests.
What Can Cause a False Positive for Fentanyl on a Drug Test?
- Cross-reactivity with certain prescription opioids
- Lab contamination
- Mishandling of specimens
- Specific substances on the fentanyl false positive list
Search queries like “what drugs can cause false positives for fentanyl” often include medications like diphenhydramine or certain antipsychotics, though these are uncommon triggers.
That’s why confirmatory testing using GC-MS or LC-MS is crucial after a presumptive positive result.
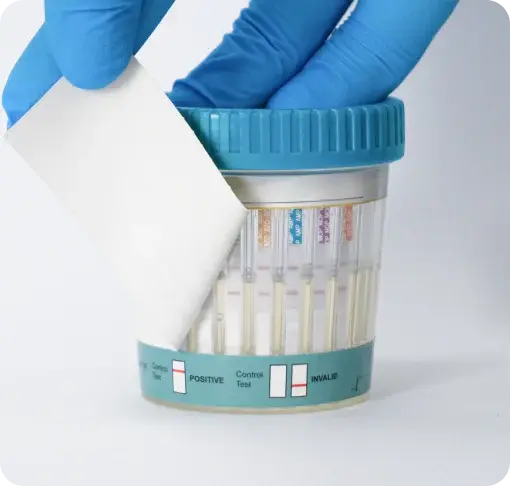
What Does Fentanyl Look Like on a Drug Test Result?
At AttoSure, our multi-panel test kits include clearly marked strip indicators. Fentanyl usually appears as FYL (or FEN depending on the test brand).
If fentanyl is detected, the result will be marked non-negative, prompting further lab confirmation.
In occupational and legal settings, a non-negative result can lead to:
- Immediate suspension (especially in safety-critical roles)
- Mandatory confirmatory testing
- Review under company or institutional drug and alcohol policies
Why Employers and Clinicians Test for Fentanyl
Fentanyl can cause severe side effects including:
- Respiratory depression
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Loss of consciousness
- Fatal overdose in small doses
Routine testing is essential for:
- Pre-employment screening
- Return-to-work evaluations
- Post-incident investigations
- Random and for-cause drug testing
- Addiction and treatment monitoring
Industries that benefit from fentanyl test strips and testing kits include:
- Healthcare
- Construction and engineering
- Education
- Manufacturing
- Transport and logistics
You can also test your knowledge with our expert-designed quizzes tailored for workplace and healthcare settings. We pride ourselves on delivering first-class educational content, created by our team of scientific experts. Browse our selection of quizzes below.
Final Thoughts
Fentanyl is one of the most dangerous opioids in circulation, and its use is on the rise. Because fentanyl side effects can be severe and workplace incidents involving fentanyl are increasing, robust drug testing protocols are essential.
You can also test your knowledge with our expert-designed quizzes tailored for workplace and healthcare settings. We pride ourselves on delivering first-class educational content, created by our team of scientific experts. Browse our selection of quizzes below.
Request a Quote